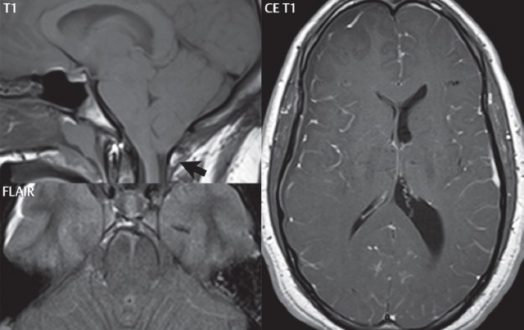
A herniation is an abnormal lump of an organ or other body part naturally or through a defect in a muscle, bone, or covering membrane. So we can say that the Uncal Herniation is a brain disease or abnormality in the brain but, before coming to its original definition, we’ll first discuss what uncus is?
The uncus is a structure that is present at the anterior medial aspect of the parahippocampal gyrus located inside the innermost part of the temporal lobe of the brain. The medial temporal region lies within the supratentorial compartment of the skull that is connected to the subtentorial chamber through the tentorium cerebelli along with the tentorial notch.
The components present inside the tentorial gap include the third cranial nerve, posterior and superior cerebral arteries, and the mid-brain. The increasing intracranial pressure causes the parts of the brain to slide from one intracranial section to another intracranial section, which leads to this disease named Uncal herniation. Till now, we have discussed a brief introduction regarding this disease. To get all the necessary detailed information related to this disease, you are requested to continue reading further.
What is Uncal Herniation?
Uncal Herniation is a subtype of transtentorial downward brain herniation involving the uncus. It occurs when there is a certain increase in intracranial pressure. This rise in intracranial pressure causes the brain’s portions to move from one intracranial section to another. In Uncal herniation, the rise in intracranial pressure causes the uncus to glide over the tentorial notch. Uncal herniation is a painful deadlier neurological disease that indicates the failure of all adaptive mechanisms for intracranial compliance.
Uncal Herniation Symptoms
A patient having Uncal herniation will observe the following symptoms.
- Headaches and Seizures
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Altered mental status
Besides these common symptoms, a patient with Uncal herniation has a lowered level of consciousness. Also, one or both the pupils of a person suffering from this disease are dilated and fail to become narrow in response to light. These symptoms help to diagnose this disease in a person.
Uncal Herniation Causes
When something inside the skull exerts pressure that results in moving brain tissues, then brain herniation occurs. Brain herniation most often happens due to severe head injuries, brain bleeding, brain swelling, strokes, and brain tumors. According to some neurologists, herniation in the brain can be a side effect of brain tumors.
Similarly, any situation that will be the reason behind the significant rise in intracranial pressure will cause this life-threatening disease named Uncal herniation. Any inflating space covering a lesion located within the skull can put a patient’s life at risk for Uncal herniation. Severe head trauma that may lead to a speedy inflating or expanding epidural or subdural hematoma can cause Uncal herniation to occur in a person.
Uncal Herniation Types
There are two major types of brain herniation classified as supratentorial and infratentorial. A supratentorial herniation is the herniation of structures that is above the tentorial gap and, an infratentorial herniation is the herniation of structures that is below the tentorial gap.
So, Uncal herniation is itself the subtype of supratentorial herniation. Uncal herniation further has no more subtypes. Other subtypes of supratentorial herniation are as follows.
- Uncal (transtentorial) herniation
- Transcalvarial herniation
- Central herniation
- Cingulate (subfalcine/transfalcine) herniation
- Tectal (posterior) herniation
There are two more types of brain herniation stated below.
- The Upward (upward cerebellar or upward transtentorial) herniation
- The Tonsillar (downward cerebellar) herniation
These are the subtypes of infratentorial herniation.
Uncal Herniation Treatment
When symptoms of Uncal herniation start to become visible, then doctors should immediately act to reduce the intracranial pressure by adjusting the volume of anyone structure of the intracranial chamber that could be a brain, cerebrospinal fluid, or blood. To achieve this strategy, the physician should do the following things:
- Lift the head of the bed to 30 degrees
- Hyperventilation
- Hyperosmolar therapy
- Keeping a midline head position
The use of Hyperventilation is to bring down the intracranial pressure by lowering arterial carbon dioxide levels. It will induce vasoconstriction to diminish the volume of cerebral blood. Doctors make the tidal volume or respiratory rate rise to achieve this.
Doctors apply Hypersmolar therapy (with mannitol or hypertonic saline) to patients when there is a doubt of brain herniation. Also, they use this therapy when a patient is having intracranial pressure elevations above 20 mm mercury.
If these clinical signs do not help reduce intracranial pressure, then the next step to manage Uncal herniation is the decompressive surgical options.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information