Learn all about thyromegaly symptoms and treatment. Thyromegaly refers to the enlarged thyroid gland. As the thyroid enlarges in size, it can lead to other symptoms. For example, a patient may begin to experience stiffness around their throat. Thyromegaly happens whenever the thyroid hormone becomes enlarged.
According to the “American Thyroid Association”, the main cause of goiter is iodine deficiency. When a person did not consume enough iodine for extended periods of time, it can lead to this condition. That’s because your thyroid gland needs iodine to function.
Thyromegaly has a considerable amount of symptoms. The swollen thyroid gland becomes visible in the outside of your neck. There will be a sensation of tightness in the esophagus area, especially when one coughs. This in turn can lead to difficulty breathing and difficulty swallowing food. Other symptoms a headache, dizziness, bad breath, and fever if there is an infection. Especially bad cases can lead to hypothyroidism where the gland stops making the thyroid hormone or hyperthyroidism where the gland produces too much thyroid hormone. If not treated this could even lead to thyroid cancer or perhaps toxic nodular goiter.
In the United States alone, there are more than 200,000 cases of goiter per year. The reason why thyromegaly is so common is because people aren’t getting enough iodine in their diet. Some common risk factors for goiter include genetic predispositions, being over the age of 40, being a woman, certain medications, radioactive substances, and lack of iodine in the diet.
Treatment is aimed at preventing the signs, symptoms, and complications of hyperthyroidism, such as heart failure, osteoporosis, and rapid heart rate. Treatments include destroying the gland using radioactive iodine (131-iodine), blocking the production of thyroid hormone with medications, or conservatively following the patient with mild hyperthyroidism. “Subclinical hyperthyroidism” refers to an adult patient with a hyperfunctioning nodule, but TSH is minimally suppressed and the blood levels of thyroid hormones are normal. Treatment is individualized based on age, the presence of other medical conditions, and patient preference.
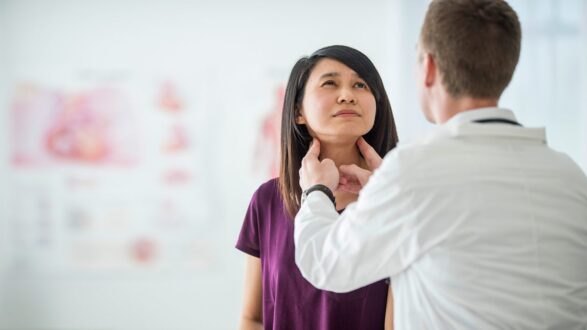
Thyromegaly (Enlarged Thyroid)
Thyromegaly is the enlargement of thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is one of the important glands in our body which secretes thyroid hormones. When the thyroid gland grows bigger than the normal size this condition is called thyromegaly or goiter. The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and is located in the lower portion of the neck just below Adam’s apple. It produces hormones that help regulate metabolism in the body.
Thyromegaly Symptoms
Thyromegaly symptoms include:
- Enlargement or swelling is visible at the base of the neck
- Tight sensation on the throat
- Coughing
- Pain in neck
- Feeling of stiffness inside the neck during coughing
- Voice hoarseness
- Difficulty in breathing
- Intolerance of high temperature
- Difficulty in swallowing food
- Indigestion
- Wight loss
- Problem in speaking
- Headache
- Bad breathing smell
- Dizziness
- Fever is associated, if infection is developed in thyroid gland
Thyromegaly Causes
Thyroid gland looks like a butterfly. Development of nodules in the thyroid gland often extended both the side of the gland causes enlargement. As previously mentioned, it’s usually the result of goiter. Following are the causes of thyromegaly:
- Insufficient iodine in the diet
- Infections
- goiter
- Graves’ disease
- Hashimoto’s disease
- Inflammation and Infiltration
- Tumors (benign/ malignant)
- Hereditary / Family History
- Selenium Deficiency
- Taking some medications
- Pregnancy
- Age and Gender (40 years older and above). Women are more high risk than men.
- Hereditary (Family History)
- Taking medicines such as cobalt or lithium
- Radiation Exposure
- Not taking food that is high in iodine content (cabbage, peanuts, peaches, etc.)
Thyromegaly Treatment
Thyromegaly treatment is the reduction of enlargement of the thyroid gland which is possible by limiting the underlying cause. Surgery is mainly recommended in case of malignancy or tumor development in the thyroid gland and cannot be effectively treated with radioactive iodine therapy or in case patient is not responding to other available treatments. Cosmetic surgery is rarely recommended in case of thyromegaly.
- Propylthiouracil and methimazole, these two drugs are often prescribed for giving the radioactive iodine therapy.
- Methimazole and Propylthiouracil are drugs which control hyperthyroidism by inhibiting the incorporation of iodine ion into the structure of T3 and T4.
- Propylthiouracil is another medicine which limits the conversion from T4 to T3.
- Levothyroxine suppressive therapy is a long-term treatment process, but it provides effective result in case of non-malignant hyperthyroidism
- Replacement of Thyroid Hormone: This treatment option is reserved for patients who have either very high or very low levels of thyroid hormone.
- Ethanol Infusion: This is an effective treatment option that used in patients who have thyromegaly that isn’t due to cancer.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information 

