What is Subhyaloid hemorrhage?
Subhyaloid hemorrhage is a medical disorder that develops when there is bleeding beneath the retina of the eye. It is the retina’s job to carry visual signals from the retina, a small layer of tissue along the back of the eye, to the brain. A subhyaloid hemorrhage is something that can develop if there is bleeding that takes place between the retina and the vitreous gel that fills the eye.
Most subhyaloid hemorrhages are caused by a sudden rise in blood pressure, which can happen when pulling weights or striving to have a bowel movement. Other probable causes include eye damage, blood problems, and certain drugs. Subhyaloid hemorrhage can cause sudden vision loss or a shadow in the affected eye’s field of vision.
Subhyaloid hemorrhage is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate medical attention to prevent irreversible vision loss. However, early detection and intervention can frequently avert major problems. Medication, surgery, or close observation to enable natural recovery are all possible approaches to treatment.
Subhyloid Hemorrhage Meaning
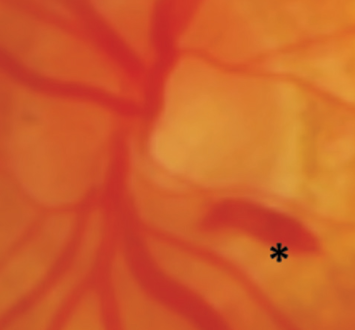
A Subhyaloid hemorrhage is an intraocular blood clot that stays contained in a newly formed space that was not there before, typically between the retina and the posterior limiting layer of the vitreous. It is therefore completely different from a vitreous hemorrhage, which has traumatic or diabetic origins as well as intraretinal hemorrhage, which is linked to conditions including hypertension and diabetes. A Subhyaloid hemorrhage is extremely unusual.
Subhyloid Hemorrhage Symptoms
A subhyaloid hemorrhage is recognized by the presence of blood that is extravasated beneath the retinal layer. They are commonly caused by acute trauma, although they are best known as a sign of SAH (Subarachnoid hemorrhage). Hemorrhages in SAH manifest as a “puff” of blood coming from the central disc.
Subhyaloid hemorrhages in the macula lead to a rapid and dramatic loss of vision. Photoreceptor toxicity can develop when the retina is exposed to hemoglobin and its catabolites for an extended period.
Subhyloid Hemorrhage Causes
A subhyaloid hemorrhage occurs when blood collects in a space between the vitreous and the retina. Subhyaloid hemorrhage possesses a wide variety of causes. In most cases, it is the result of damage to the retinal blood vessels brought on by conditions like atherosclerosis, retinal arterial macroaneurysm, diabetic retinopathy, hypertension, retinal artery or vein occlusion, chorioretinitis, blood disorders, and shaken baby syndrome or traumatic injury. It can also happen as a result of a retinal vascular rupture caused by physical effort or general anesthesia, as well as Terson syndrome or Purtscher retinopathy.
Subhyloid Hemorrhage Treatment
Subhyaloid hemorrhage is treated conservatively if the macula is not affected; however, if the macula is affected, an epiretinal membrane is often formed, leading to permanent vision loss due to alterations in the macular retinal pigment epithelium and perhaps toxic damage to the retina. Subhyaloid hemorrhages can also be treated with pars plana vitrectomy and pneumatic displacement of the hemorrhage. A retinal detachment or the development of cataracts are possible side effects of these operations.
Nd: YAG laser hyaloidotomy is a noninvasive method that enables quick drainage of the occluded macular area and improved eyesight within a single day. However, it is crucial to think about reported complications, such as vitreomacular traction syndrome and macular holes.
Choosing a treatment is difficult because the literature comparing the various treatment techniques is still incomplete.
When thinking about Nd: YAG laser hyaloidotomy, it’s important to have good clinical judgment, use the right technique with good visibility, make sure the hyaloidotomy is in the right place, be careful with the laser energy, and pay attention to the timing of symptoms to get the most out of the added photo disruption. If the laser therapy is delayed, the blood clot under the internal limiting membrane can form, causing the procedure to fail or only be partially successful.
Preretinal hemorrhage vs Vitreous Hemorrhage
Preretinal hemorrhage is a known problem that is associated with diabetic retinopathy. In contrast, the presence of blood in the vitreous humor constitutes vitreous hemorrhage. A minor quantity causes vision blurring. Large volumes of blood can cause the vitreous humor to become opaque, resulting in near-complete vision loss.
Typically, preretinal hemorrhage is induced by bleeding of the new vessels as a result of hyaloid traction. Vitreous hemorrhage, on the other hand, can occur as a result of both a localized condition affecting the structures of the eyes and other illnesses that affect the body.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information