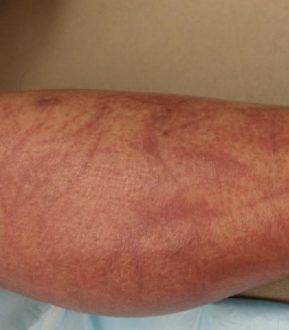
Shiitake Dermatitis is also known; by various names like toxicodermia and flagellate erythema. Shiitake mushroom dermatitis or Shiitake dermatitis is a kind of pruritic dermatitis first described in 1977 by Nakamura. This condition is characterized; by millimeter-sized linear, erythematous, pruritic streaks resembling whiplash marks. Chinese and Japanese states have the highest consumption rates of shiitake mushrooms and the highest prevalence of shiitake dermatitis. Shiitake dermatitis affects around 2% of the population consuming raw mushrooms or improperly cooked mushrooms. All ages are affected by this mushroom; however, the condition is more frequent in males than females. Today, the majority of the cases are diagnosed in several other countries where the use of this mushroom is increasing day by day.
Although Shiitake dermatitis is rare outside China and Japan, there is a well-known relation between shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) and flagellate dermatitis ingestion. In addition to that, bleomycin intake may also lead to similar findings.
Shiitake Dermatitis Symptoms
The clinical features can appear within a couple of hours and persist up to 5 days right after the intake of these mushrooms.
Other clinical features associated with this condition include swelling affecting mainly the trunk, but it may also influence the neck, limbs, and head. It usually does not affect mucosal surfaces. The rashes may get worse after exposure to sunlight. Gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur indicating the progress of this condition. The onset symptoms of this condition are not restricted.
Individuals affected by this dermatitis may show several other symptoms too. Those symptoms may involve fever, diarrhea, tingling of both the feet and hands. Affected individuals may also exhibit symptoms; malaise, edema, and difficulty in swallowing meals. After eating uncooked shiitake mushrooms, a few individuals may also show an unusual lip-tingling after approximately 48 hours of consuming the concerned mushroom. It may also be caused; by consuming fully cooked shiitake mushrooms.
Shiitake Dermatitis Causes
Shiitake Dermatitis is a kind of skin eruption quite similar to whiplash marks and develops after eating raw shiitake mushrooms. Flagellate dermatitis is a toxic reaction to a substance, lentinan. Lentinan is a polysaccharide derived from the vegetative portion of the edible Japanese shiitake mushroom. This substance is also available in powdered, fresh, or lightly cooked shiitake mushrooms. Lentinan activates interleukin-1 secretion that leads to hemorrhage, vasodilation, and rash.
This hypothesis is supported; by an observation that shiitake dermatitis is not visible with the intake of thoroughly cooked mushrooms at a temperature greater than 145 degrees centigrade. The median known time for the symptoms of this condition to show from the ingestion of shiitake mushrooms is usually 24 hours, ranging between 12 hours to 4 days. Most of the patients recover after three weeks with or without any treatment. Flagellate or shiitake dermatitis does not develop due to cutaneous contact with the mushrooms.
Shiitake Dermatitis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this mushroom-related condition is clinical, based upon the characteristic history of the recent mushroom intake and the appearance of the rash itself. There are usually no particular laboratory findings. However, the usual tests may include; urea and electrolytes, total blood count, and liver function tests. The histopathology describes spongiosis, dermal edema, focal hyperkeratosis and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with eosinophils.
Dermatomyositis and adult on Still disease are associated with the differential diagnosis of shiitake dermatitis. However, drug reactions to peplomycin, docetaxel, and bleomycin are also essential in differential diagnosis. Raw shiitake mushrooms may also rarely cause allergic dermatitis in sensitized individuals. The characteristic skin lesions of shiitake dermatitis usually appear as streaky, linear, and urticarial papules that are more frequently observed; on the trunk and extremities.
Shiitake Dermatitis Treatment
The treatment method for dermatitis may vary based upon the cause and symptoms. Besides the home remedies, treatment methods may involve the application of corticosteroid ointments or oral medications, calcineurin inhibitors, exposure of the affected region to artificial light, and use of wet dressings.
When it comes to shiitake flagellate dermatitis, it is a self-limiting condition. It is usually unknown whether the treatment speeds up the resolution of the rash. The treatment is done; with the use of topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. Affected individuals must ensure that; they protect their skin from sun exposure while the rash is resolving. Most of the time, the improvement is evident within two days and complete resolution after three weeks. Besides treatment methods, the target should be to minimize all of the causes associated with this condition. Future attacks may be prevented; by ensuring that shiitake mushrooms are cooked thoroughly before consumption.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information