Learn all about pure hypercholesterolemia (elevated cholesterol levels in blood) the signs and symptoms of it and treatment options. Pure Hypercholesterolemia which is also known by the name of Familial Hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition in which people have a tendency to have high cholesterol or lipid levels genetically.
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that occurs naturally in the body. It performs several vital functions. It is needed to make the walls surrounding the body’s cells and is the basic material that is converted to certain hormones. The fat and cholesterol are absorbed in the intestine and transported to the liver. The liver converts fat into cholesterol, and releases cholesterol into the bloodstream. There are two main types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (the “good” cholesterol).
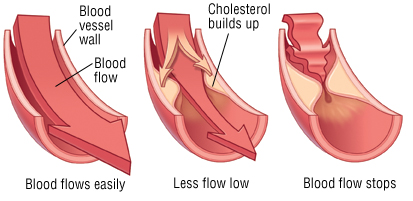
High levels of LDL cholesterol are linked to atherosclerosis, which is the accumulation of cholesterol-rich fatty deposits in arteries. Because high cholesterol levels can cause atherosclerosis, doctors recommend that people keep their cholesterol levels within a specific range. In general, adults older than 20 should try to keep their total cholesterol level below 200 milligrams per deciliter.
About 1 out of every 500 people has an inherited disorder called familial hypercholesterolemia, which can cause extremely high cholesterol levels (above 300 milligrams per deciliter). People with this disorder can develop nodules filled with cholesterol (xanthomas) over various tendons, especially the Achilles tendons of the lower leg. Cholesterol deposits also can occur on the eyelids, where they are called xanthelasmas.
Avoid processed foods, especially those that contain saturated fats. Instead eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, whole-grain breads and cereals, and low-fat dairy products. The initial treatment of high cholesterol should always be lifestyle changes. This means altering your diet and getting more exercise. Some people respond dramatically to dietary changes. The effectiveness of following a healthy diet and using medications to lower cholesterol varies from person to person. On average, diet and exercise can lower LDL cholesterol by about 10%. Medications can lower LDL cholesterol by another 20% to more than 50%.
What is Pure Hypercholesterolemia?
Pure hypercholesterolemia refers to a condition in which people have a genetic tendency for high cholesterol or high lipid levels. High cholesterol can boost a person’s chances for developing heart disease and other conditions. An excess of fatty deposits in blood vessels can make it hard for blood to flow through arteries. Pure hypercholesterolemia, also called familial hypercholesterolemia, is an inherited condition that might raise unhealthy cholesterol levels. Molecular studies identified two genes that prevent the body from metabolizing low density lipids (LDL) efficiently. Pure Hypercholesterolemia or Familial Hypercholesterolemia is an autosomal dominant trait meaning that the defective gene needs to be passed by just one parent in order to get this condition. If the gene is inherited from both parents then this condition becomes that more severe and may predispose the patient to heart attacks and other cardiac conditions even in childhood.
Pure Hypercholesterolemia Definition
Hypercholesterolemia, also called dyslipidemia, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of high blood lipids and “hyperlipoproteinemia” (elevated levels of lipoproteins in the blood). Hypercholesterolemia refers to levels of cholesterol in the blood that are higher than normal. Having high levels of cholesterol predisposes an individual towards cardiac conditions along with some other potential complications. Due to high cholesterol levels, there are excessive fatty deposits in the vessels which make it tough for the blood to flow through arteries because of which the heart is deprived of the oxygen rich blood that it normally requires for normal functioning causing a heart attack. A stroke may also occur due to low blood flow to the brain due to the fatty deposits.
Pure Hypercholesterolemia Symptoms
Pure hypercholesterolemia does not show any symptoms in early stages; however some of the symptoms are as under;
• Fatty skin deposits over parts of hands, elbows, knees, ankles, and around the cornea of eye.
• Cholesterol deposits in the eyelids
• Chest pain or other symptoms of a coronary artery disease at a very young age.
Treatment of Pure Hypercholesterolemia
Pure hypercholesterolemia treatment depends on its elevated levels. However, a statin drug should almost always be the first choice to lower LDL cholesterol.
• Statins are also called HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. They include lovastatin (Mevacor), simvastatin (Zocor), pravastatin (Pravachol), fluvastatin (Lescol), atorvastatin (Lipitor), pitivastatin (Livalo) and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
Other cholesterol-lowering medicines include:
• Cholestyramine (Prevalite, Questran)
• Colestipol (Colestid)
• Colesevelam (WelChol)
• Ezetimibe (Zetia)
• Fibrates (such as gemfibrozil or fenofibrate)
• Nicotinic acid
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information