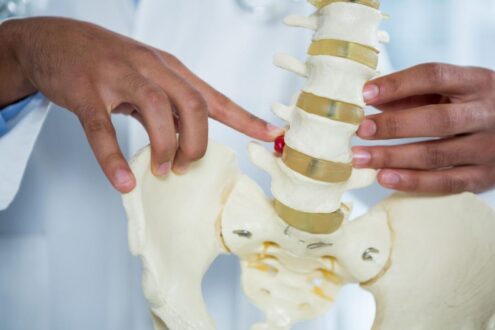
Polyradiculopathy is commonly called as “pinched nerve”. It is a condition “which affects more than one nerves which leads to many neuro problems such as pain (radicular pain), weakness, loss of control of muscles, and numbness”.
This problem majorly affects the root part of the nerves near the exit point from the spinal cord. But the resulting problems occur in the connected organs of the body where these nerves are penetrating. For example; if a nerve is enrooted from neck then a defect in this particular nerve can cause symptoms in the arm. Likewise, if a defected nerve is enrooted form lower back then it can manifest problems in the foot.
Radicular pain is sometimes confused with referred pain which needs a proper distinction as both are quite different form each other in every aspect. Referred pain is the reflection of pain at some other location than the site of stimulus but the radicular pain is the appearance of the symptoms in different organs depending upon the penetration of the defected nerves.
Polyradiculopathy Symptoms
Symptoms for this particular condition may vary from patient to patient and these are not the same for all. But the most common signs and symptoms include;
- Spreading pain in the different organs of the body such as arm, neck, chest, upper and/or back shoulders etc.
- Numbness.
- Tingling in fingers or hands.
- Muscle weakness is also experienced in many patients.
- Lack of co-ordination between different body organs especially limbs.
Polyradiculopathy Diagnosis
Mostly the diagnosis is carried out by physical examination as there is no proper tests for the identification of the disease. In this case signs and symptoms are considered very crucial to understand the state of disease.
Usually those patients who show any signs of this disease are initiated on the drug therapy of this particular disease and if the symptoms get better with the time then it gives the indication of right decision of diagnosis. This practice is very common for the diagnosis of the polyradiculopathy.
Often this disease has been confused with the Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) as both share same symptoms such as pain and numbness but these two are differ when it comes to the appearance of the symptoms after illness. As GBS linked to illness but polyradiculopathy is not.
Polyradiculopathy Causes
Usually the nerve damage happens as a result of high pressure directed from the material of bone rupturing. When the degeneration of the bones happen the material separates out and puts high pressure in the different areas of nerves nearest to the degenerative location. Arthritis can also cause the pressure on nerve roots.
These causes varies in different ages as in middle-aged population normal degeneration occur in the discs and this pressure leads to the nerve damage. Meanwhile in the younger people, normal degeneration usually doesn’t exist so the damaged discs happen as a result of any trauma which leads to the nerve damage particularly in the area of injury. When the trauma causes the bone rupture the separated out material inserts pressure on the nerve roots and leads to pain.
Polyradiculopathy Treatment
Polyradiculopathy can be treated in two different ways either by drug therapy or by Physical therapy.
Drug therapy
It includes a combination of pain relieving medications from two pharmaceutical classes such as; corticosteroids which are considered the strong anti-inflammatory products, and non-steroidal pain relieving drugs including ibuprofen or naproxen. Usually the steroids are prescribed either orally or injected in the epidural region which is the membrane surrounding the spinal cord or generally called the space surrounding the dura.
Physical therapy
It is considered to be the most suitable option for pain reduction in polyradiculopathy patients as the basic requirement in these patients is the management of the pain. Mostly it includes the cervical traction and mobilization, exercises and other modalities.
In some cases, compression on the nerves is really high that it leads to the motor weakness and results in unbearable pain that could not be treated with either of the above stated therapies. So in this situation surgery is the only option left to manage the pain in these patients.
Before the initiation of any therapy the proper diagnosis and recommendation of the therapy is required by the concerned physician. Without prescription no medications should be administered by the patient.
Polyradiculopathy vs. Polyneuropathy
These two conditions vary in their causes and symptoms as well. As polyneuropathy can be adopted due to any untreated condition such as vitamin deficiency or diabetes etc. along the external trauma. But polyradiculopathy is only caused due to inner or outer degeneration of the discs or bones. Meanwhile inflammation is experienced in the polyneuropathy as it does not exit in polyradiculopathy.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information