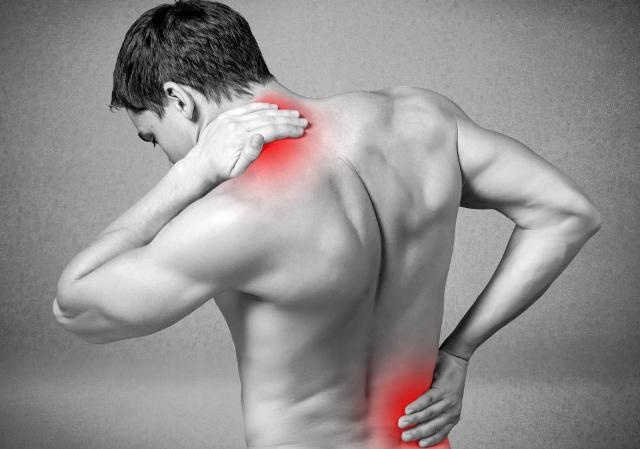
Learn all about myalgia and myositis relief from muscle pain its causes and symptoms and all about its treatments. Myalgia and Myositis are associated with muscle pain, inflammation, soreness and muscle aches in different parts of the body.
Myalgia and myositis may occur either together or independently. Painful muscles are not always inflamed. Likewise, muscle inflammation sometimes causes weakness instead of pain. Causes of myalgia and/or myositis range from localized muscle injury to systemic disorders.
Localized muscle injury includes overexertion (such as after unaccustomed exercise or following the intense contractions of a seizure), trauma to the muscle by over stretching or overloading (strains and sprains), and direct injury to the muscle (bruises, cuts, or crushing injuries).
Myalgia can also be the result of certain endocrine and metabolic disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, Addison’s disease, hypoparathyroidism, diabetes mellitus, and diabetic neuropathy. Connective tissue diseases (also called collagen vascular diseases) are a group of inflammatory disorders whose symptoms may include myalgia and myositis such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous, Polymyositis, Dermatomyositis, and polymyalgia. In central nervous system (CNS) disorders, myalgia may be related to spasticity (multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal cord injuries) or rigidity (Parkinson’s disease).
Almost everyone has sore, aching muscles now and then. Muscle pain can involve a small area or your whole body, ranging from mild to excruciating. Systemic muscle pain throughout your whole body is more often the result of an infection, an illness or a side effect of a medication.
The gait, posture and coordination are observed for any abnormal movements. Muscles are inspected for any evidence of wasting (atrophy); enlargement (hypertrophy) or permanent shortening (contracture). A muscle biopsy may be indicated in the diagnosis of inherited metabolic disorders, connective tissue disease, eosinophilia-myalgia, sarcoidosis, and trichinosis.
Myalgias and Myositis Muscle Pain
Myalgia, or pain of the muscles, is a fairly common occurrence that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. Muscle pain may occur when individuals stand for long periods of time or overuse muscles during exercises or weight lifting. This pain may occur in any part of the body depending on the cause. Some of the most commonly affected areas include the back, legs, neck, and hands. Myositis is most commonly caused by things like injury, infection, drugs and inflammatory conditions. Symptoms associated with myositis include pain, redness of the affected area, heat, and swelling.
Myalgia definition
Myalgia is a term which is derived from two words; Greek ‘myos’ meaning ‘muscle’ and ‘algos’ meaning ‘pain’. Myalgia can be defined as muscle pain or muscle ache. It is also known as ‘myoneuralgia’. Myalgia is the pain in one or more than one muscle. Myalgia is a term used to describe muscle pain and tenderness. Myalgia signifies a prolonged pain of varying intensity that may be localized or widespread, which can affect any striated skeletal muscle.
What is Myalgia?
Myalgia or muscle pain is a symptom of many diseases and disorders. Myalgia is not a disease itself but a symptom signifying an existing underlying condition. Myalgia is the pain which can affect almost any part of the body including the neck, hands, legs and the back. Myalgia is basically non-serious and non-threatening but can be discomforting. Myalgia is of different types which define the part of the body which is being affected. Some types of myalgia are as under:
- Epidemic Myalgia also known as Bornholm disease
- Fibromyalgia
- Trapezius myalgia
- Polymyalgia rheumatic.
Myositis definition
Myositis is a medical term that describes inflammation of muscle tissue “myos” being a prefix denoting muscle, and “itis” being a suffix denoting inflammation of tissue. Putting them together gives “Myositis”, i.e. muscle inflammation. Myositis is defined as the inflammation of muscle, especially a voluntary muscle characterized by pain, tenderness and sometimes spasm in the affected area. Myositis is the term for anyone of the group of inflammatory disorders. Many different etiologies of myositis include infection, autoimmune conditions, genetic disorders, medication adverse events, electrolyte disturbance and diseases of endocrine systems.
What is Myositis?
In every-day life, inflammation is most commonly experienced as the swelling around the site of wounds and around the muscle and joint injuries. But, with the conditions known collectively as Myositis, the inflammation is within the muscle tissue as a chronic autoimmune response. Myositis is a rare disease in which the muscle fibers and skin are inflamed and damaged. There are several types of myositis that affect different parts of the body. All forms of myositis involve persistent muscle inflammation, resulting in muscle weakness, swelling, and pain of the muscles. Multiple parts of the body can be affected by myositis, including the joints, heart, lungs and skin. Myositis (meaning “muscle inflammation”) is a rare disease. It includes conditions known as:
- Polymyositis
- Dermatomyositis
- Inclusion body myositis.
- Juvenile myositis
Muscle Soreness Symptoms
A description of the muscle soreness symptoms should include location, severity, and quality (dull, aching, cramping, stiffness, weakness). Individuals may report a precipitating event such as trauma, insect bite, drug ingestion, or recent immunization. Other symptoms may include fever, chills or sweats, weight loss, joint pain or stiffness, neurological symptoms (numbness, tremor, visual disturbances, ringing in the ears), depression, sleep disturbances, fatigue, rash, or respiratory, cardiac, or gastrointestinal symptoms. The history should include information regarding the onset (sudden or gradual) and type (constant or intermittent) of symptoms.
Muscle Pain Relief from Myalgia and myositis
Myalgia or Myositis treatment depend on the specific diagnosis. Nonspecific myalgia (due to overexertion, systemic viral infection, or immunization) can usually be relieved by over-the-counter analgesics. Motrin (Ibuprofen), Ultram (Tramadol), Aleve (Naproxen) may be prescribed by the physician to get relief from muscles pain. In the treatment of myalgia of effective physiotherapy, the doctor may recommend ultraviolet radiation of the affected zones, electrophoresis with novocaine or histamine.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information