Hand-Schuller-Christian illness is a unique disorder in which the body develops lipids. These lipids combine with immune cells called histiocytes to produce granulomas in numerous regions, such as the epidermis, skull, and many internal organs. This disease is characterized as a multifocal uni system disease. This feature of the disease shows that it affects organ systems, almost always bones.
Hand-Schüller-Christian illness is a clinically intermediate manifestation of a variety of histiocytic disorders. It is linked with lytic bone lesions, diabetes insipidus, and proptosis. This disease primarily affects children, young and elder people are rarely affected. The sickness is quite uncommon. It is most prevalent between two and six years of age. The disorder is potentially fatal in certain persons.
Anemia, bone marrow destruction, and respiratory issues are among the most common symptoms of this disease. The treatment of the disease is tailored to each patient’s unique symptoms and may involve the administration of medication, participation in radiation therapy, or the performance of surgical procedures.
The systemic manifestations of this condition include hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, dermatological, gastrointestinal, renal, and pulmonary involvement. Convulsions, intracranial hypertension, focal neurological impairments, mental retardation, hearing loss, and tremors are Central Nervous system symptoms. The engagement of the hypothalamus and pituitary delay sexual maturity and bone growth. This is often seen in children and young adults.
Hand Schuller Christian Disease Symptoms
Patients with Hand-Schuller-Christian disease possess a wide range of symptoms that make a diagnosis of the disease difficult. Anemia, irregularities in blood cells, and excessive bleeding are a few examples of the various types of blood-related issues that people with this disease possess. Skin disorders, such as a rash or elevated skin lesions that are pigmented, scaly, or oily, also arise for unknown reasons. People who suffer from this condition usually exhibit symptoms such as swollen gums and the loss of teeth at an early age.
Some of the more serious signs of Hand-Schuller-Christian disease are diabetes, thyroid problem, or breathing difficulty. Sometimes, lymph nodes get bigger or the pituitary gland gets hurt. Infections, vision abnormalities, and varying degrees of neurological impairment are also common symptoms. Due to the vast variety of probable symptoms and the rarity of this disease, it takes several months or more to make an appropriate diagnosis.
Some other symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- Unsteadiness, uncoordinated bodily motions, and difficulty walking.
- Speaking difficulty.
- Changes in personality or conduct.
- Memory issues.
- Bloody stools.
- Diarrhea.
Hand Schuller Christian Disease Causes
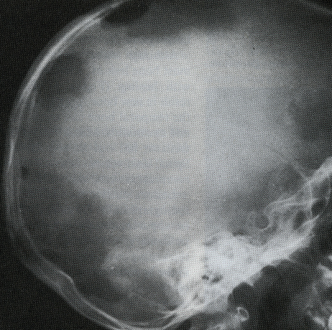
The actual cause of Hand-Schuller-Christian disease is unknown, and several blood abnormalities are present. The typical onset of symptoms occurs between the ages of three and six years old, and boys are affected by the condition marginally more often than females. Diabetes insipidus and skeletal abnormalities are frequently observed in patients with this condition. The patients mostly complain about the unnatural protrusion of the eyes. CT scans are especially useful for detecting and characterizing bone lesions as well as soft tissue involvement.
MAPKinase mutations are responsible for the development of Leukemia and Hand Schuller Christian disease. BRAF (65-70 percent), MAP2K (20 percent), and other uncommon genes are among the genes altered in this pathway, which together lead to aberrant activation of the ERK gene. This disease is mostly inherited.
Hand Schuller Christian Disease Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disease is made through the following techniques:
- Hearing tests.
- Urine osmolality.
- Chest X-ray.
- Skeletal survey.
- Bone marrow aspirates.
- Coagulation studies.
- liver and renal function tests.
- Tissue biopsy.
- MRI.
- PET scan.
Hand Schuller Christian Disease Treatment
Individual symptoms of Hand Schuller Christian illness are usually treated first, such as administering iron supplements for people who are anemic. In some of the worst cases, more intensive treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation, are needed. To remove huge tumors or to cure any internal damage produced by the development of this disease, surgical treatment is mostly utilized as a potential treatment option.
The treatment options that are mostly available for this disease are; observation, radiation therapy, photodynamic therapy, Immunotherapy, targeted treatment, other types of medication, and transplantation of stem cells.
Scraping is used to treat localized types of the disease, where bone alterations are seen. Disseminated forms respond to glucocorticoids or chemotherapy, particularly cyclophosphamide, and methotrexate. Neuroendocrine symptoms of the condition generally do not return to normal under the impact of such medication.
It is desirable to treat patients in clinical trials rather than in regular care. The age of the patient at the time of presentation, the degree to which the disease spread throughout the body, and the patient’s reaction to treatment are the elements that determine the prognosis for this illness.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information