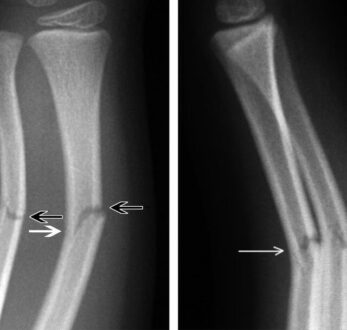
Fracture is referred to as the stress applied on a bone that is higher in magnitude than the bearing strength of the bone. This damage to the integrity of bones is seen in all age groups involving children, teenagers, and adults. A fracture is categorized into two major types that are displaced fractures in which bone moves away from its initial position on the application of stress, and non displaced fracture in which bone remains at its exact position on the application of stress. However, the sub-types of fracture may include greenstick fracture, nightstick fracture, transverse fracture, spiral fracture, Oblique fracture, Compression fracture, and others.
This article primarily consists of all the relevant details regarding the greenstick fracture and nightstick fracture. So, to get more insights into these two sub-types of fractures, proceed reading further.
Greenstick VS Nightstick Fracture
Greenstick fractures are referred to as “Long bones Fractures.” They’re the mild fractures that are commonly seen in younger children lying under the age group of 10 years. These fractures usually take place in long bones that incorporate fibula, tibia, ulna, radius, humerus, and clavicle. Most ordinarily, these non-complete fractures are seen in the forearm and arm, immersing either the ulna, humerus, or radius. These fractures are a result of the disconnection of the cortex and periosteum on one side of the bone, while they remain connected on the other side of the bone.
These sorts of fractures are basically partial fractures that occur ordinarily after a fall on an outstretched arm. Some other reasons may include malnutrition, motor vehicle crashing, sports harms, or sudden traumas such as the child is bashed with a harmful object. However, nightstick fractures refer to “Ulna Shaft Fractures,” in which forearm damage takes place. These fractures are a result of the application of stressful objects or victims’ attempts to defend themselves from assaults. Some other reasons may include vehicle collisions and falls. From the studies, it is reported that Ulnar fractures ordinarily take place in teenagers and above the twenties, in which 80% of injuries were due to direct blow.
Greenstick vs. Nightstick Fracture Difference
Although both types of fracture possess many similarities, they’ve some dissimilarities as well. So, let’s have a brief insight into the differences between greenstick vs. nightstick fractures.
Greenstick fractures are the partial fractures in which the bone remains in its alignment. These fractures are ordinarily seen in younger children possessing the age group of 10 years. These fractures take place in long bones such as fibula, tibia, ulnar, radius, humerus, and clavicle. However, nightstick fractures take place only in ulnar bones and are ordinarily seen in teenagers and above twenties age groups.
Greenstick fractures mainly occur due to the deficiency of vitamin D, motor vehicle crashing, sports harms, and sudden traumas. However, nightstick fractures mainly occur due to the harm caused by assaults or by vehicle collisions and falls.
Greenstick fractures are non-completed fractures with cracks on the forearm and can be healed by non-operative treatments. However, nightstick fractures are severe fractures with a broken forearm and require operative treatments in some cases.
Greenstick vs. Nightstick Fracture Symptoms
The signs of greenstick fractures are sometimes confused with bruises or sprains. If these fractures are less severe, then mild pain and tenderness will take place. But, if the greenstick fracture is more severe than intense pain, swelling, and damage will take place. However, in the case of nightstick or ulna fracture, significant tenderness, intense pain, swelling, bruising, and obvious deformity occurs.
Greenstick vs. Nightstick Fracture Causes
Greenstick fractures are primarily caused by a fall on an outstretched arm, deficiency of vitamin D, accidental collisions, sports harm, or sudden traumas such as the child is stuck with a harmful object, etc. However, nightstick fractures are primarily caused by severe vehicle accidents, falls, or defensive action against assaults.
Greenstick vs. Nightstick Fracture Treatment
The treatment for greenstick fracture mainly depends on its severity. If the damage is not severe, then basic treatment can be done, such as medication and simple plaster will heal the damage. But, if the fracture is severe, then you need to consult the orthopedic immediately to reduce the risk of complications.
Orthopedic will first observe the degree of angulation. If it’s at a higher stage, then immobilization and casting will be done. The kind of cast depends on the position of the fracture. Short arm casts are preferred for distal fractures, while long arm casting is done for proximal fractures. The healing time for a greenstick fracture depends on the age of the child. If the child is under ten years, then he will recover soon. But, if the child is above ten years, then the recovery will take some time. Commonly the healing time for greenstick fractures is 4-8 weeks.
However, in the case of nightstick or ulna fractures, the immobilization of bone is done with the assistance of bracing or casting. But, if there is a significant dislocation of a fracture, then the operation is necessary for fixing the damaged bone. The ulna operations are usually done by placing screws or plates.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information