Learn all about fovea palatinae pain, location, purpose, swollen.
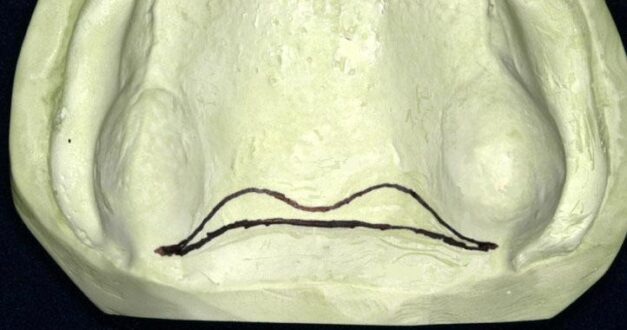
The fovea palatinae are two pinpoint-like markings that are located anterior to the junction of the soft and hard palate. They have no particular function, but they are useful for dentists when we are making a set of dentures, as an anatomic location, since it is generally around 2 mm ahead of the soft palate.
Anterior vibrating line is an imaginary line located at the junction of the attached tissue overlying the hard palate and the movable tissue of the immediately adjacent soft palate, visualized while the patient is instructed to say ‘;ah’ with short vigorous bursts. Posterior vibrating line is an imaginary line at the junction of the aponeurosis of the tensor veli palatine muscle and the muscular portion of the soft palate visualized, while the patient is instructed to say ‘ah’ in short bursts in a normal unexaggerated fashion. Although the vibrating line is not truly an anatomical features. It is very important to locate for proper construction of the maxillary complete denture. In a study the distance between the anterior and posterior vibrating lines varied between 2 and 8 mm. The distance between the foveae palatinae and the vibrating line can vary according to the configuration of the soft palate; that is, a soft palate with a less steep slope could be expected to be longer, implying that a broader posterior palatal seal could be achieved.
It aids in determining vibrating line. These landmarks provide a guide to the position of posterior palatal border of a denture.in patients with thick ropy saliva the fovea palatine should be left uncovered or else the thick saliva flowing between the tissue and denture can increase the hydrostatic pressure and displace the denture.
In many cases, the swelling or inflammation you’re experiencing will go away on its own. More severe causes for swelling of the roof of your mouth, such as cancer, are rare. It’s more likely that you’ve irritated the delicate skin on your hard palate. As you recover, remember to give your skin time to heal. Don’t eat extremely hot or hard food while your skin is already sensitive, and avoid foods that irritate the roof of your mouth. If the swelling doesn’t go away in five days to a week, you should see your doctor.
What is Fovea Palatinae?
These are two small depressions in the posterior aspect of the palate, one on each side of the midline, at or near the attachment of the soft palate to the hard palate. It is formed by coalescence of the duct of several mucous glands. The position of fovea palatine also influences the posterior border of denture. The secretions o fovea spreads as a thin film on denture therefore aiding in retention.
Fovea Palatinae Pain
Pain will accompany swelling in the roof of your mouth. Some of the conditions that could cause pain are serious. These conditions include oral cancer, alcohol-related liver disease, and hepatitis. Many canker sores develop on your cheek or the gums near your teeth, but it’s not uncommon for them to appear on the roof of your mouth, too. A common virus called the herpes simplex virus causes cold sores. Most cold sores last about a week and disappear without treatment. Typically, cold sores appear on your lip, but they may crop up on your hard palate.
Fovea Palatinae Location
Clinical, radiographic, and histologic studies of the fovea palatini indicate that they were positioned 1.31 mm. (mean of 100 subjects) in front of the vibrating line. Radiographically and histologically, the foveae were located in soft tissue covering the hard palate in all specimens. Histologically, complex nerve endings were found just anterior to the foveae and spreading to the soft palate. The findings were related to clinical aspects of complete dentures.
Fovea Palatinae Purpose
The fovea palatinae are two small indentations that lie bilateral to the midline of the palate, at approximate junction between the soft and hard palate. They denote the sites of opening of ducts of small mucous glands of the palate. Post palatal seal is another anatomical landmark which helps in retention of maxillary dentures. It is a soft tissue area at or beyond the junction of the hard and soft palates. It is also considered to lie between anterior and posterior vibrating line.
Fovea Palatinae Swollen
Fovea palatine swelling on the roof of the mouth may be due to several potential causes, most of which will resolve with minimal treatment. In less common cases, the swelling may be due to a more serious condition. Other symptoms may accompany the swelling, including:
- blisters or other sores
- dry mouth
- muscle spasms
- Pain or discomfort.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information