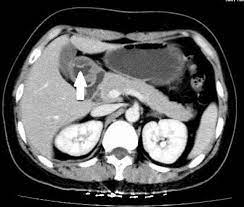
The duplication of the alimentary canal is considered a rare congenital abnormality. Sometimes this condition is asymptomatic and can occur anywhere in the mouth and anus. Most of the time foregut duplication cysts are diagnosed incidentally. The term foregut duplication was initially introduced by W.E. Ladd.
This duplication is benign most of the time. But if the treatment is not proper it might advance into malignancy. It can be associated with ectopic gastric mucosa. There are variations in size. But majorly the duplication is single and is spherical. The problems associated with foregut duplication are seen in the early days of childhood.
As this condition is not frequently observed, the clinical features and the management or treatment plan are still under discovery. However, there are several clinical pieces of research that state the details. Here we will explain the foregut duplication cyst, so keep reading further.
Foregut Duplication Cyst Location
There are multiple locations involved in the formation of a foregut duplication cyst. More than one theory has mentioned different locations. Few clinical researchers believe that the development of split notochord is the primary defect of the development of the cyst in the gut between the half of the vertebrae.
The spherical structure of the cyst is associated with the alimentary canal and bowel. The smooth muscle wall of these locations is the same. Hence, people suffering from the foregut duplication cyst will present with more than one symptom. It is a bit daunting to spot the location sometimes.
The blood supply is common between the cyst and the location. An ileal duplication cyst is a common form followed by esophageal duplication. Moreover, foregut duplication cyst can occur anywhere between the mouth and anus. There is no confirmed site or location. The patients should discuss with their doctor if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Foregut Duplication Cyst Symptoms
The symptoms of foregut duplication cyst depend on a variety of factors. These factors include the following:
- Location
- Size
- Type of duplication
- Is there a presence of heterotopic mucosa
A patient usually experiences a wide range of symptoms such as:
- Abdominal pain is common
- Abdominal distension
- Mild to severe internal bleeding
- Obstruction
- Respiratory problems
- Pain can be a symptom but in asymptomatic conditions it is painless
- Airway obstruction
- Feeding difficulties
- Palpable mass
- Peptic ulcer with hemorrhage
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Diarrhea or constipation which can be acute or chronic
Usually, a patient with a foregut duplication cyst has no symptoms and doctors find out about it during the regular medical check-up. But if any patient presents any signs and symptoms there are usually two or more. In most cases, the patients ignore the symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea and consider it normal.
The benign nature of the cyst makes it non-discoverable unless the patient undergoes clinical or radiological tests.
Foregut Duplication Cyst Causes
The cause of the foregut duplication cyst is still unknown. It is believed that embryological aberrations are the cause of these cysts. According to the latest clinical research, there is a diverticulum in the embryo. As the body grows the diverticulum can grow in size too. The persistent nature of the diverticulum can grow as long as the alimentary tract, causing all the symptoms and obstruction.
The excessive growth will eventually lead to the duplication of the foregut. The justification is fair enough to explain the cause of this condition. The incomplete twinning leads the cysts. This rare condition can be painless or painful depending on the size and location of the cyst.
Genetics can be another cause. If someone from the family has had this condition before. They might be diagnosed with foregut duplication cyst. However, few studies are found regarding this.
Foregut Duplication Cyst Treatment
The first-line treatment of foregut duplication cyst is surgery. Two surgical approaches can be adopted, either laparotomy or laparoscopic. It depends on the patient’s condition. Antenatal ultrasound can help to diagnose foregut duplication cyst at an early stage.
The surgery is not only preferred due to the malignancy but if the condition is left untreated it might lead to severe complications. Moreover, symptomatic patient cases are always recommended with surgery.
After the surgery, the recurrence rate is minimal and the quality of life is enhanced. Some cases have complicated surgeries due to the location or size of the cyst. X-ray and CT scans are used to diagnose foregut duplication cyst.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information