Kounis syndrome, also known as allergic angina, is a collection of coronary symptoms, including concomitant chest pain, brought on by mast cell mobilization as a result of sensitivity or a strong immunological reaction to a chemical or combination of drugs. The Kounis syndrome is quite uncommon. This disorder is defined as a severe coronary condition caused by an adversely responsive reaction or a strong resistance to a substance such as a drug or extra substance (side effects include chest pain associated with decreased blood flow to the heart).
Numerous things can set off an attack, such as adverse drug reactions, contact with radiological contrast medium, bee stings, shellfish, and coronary stents. Kounis syndrome includes other arterial systems with comparable physiologies to those of the coronary arteries, such as the mesenteric and cerebral circulation.
Kounis Syndrome Symptoms
Kounis syndrome is defined by a collection of signs that appear as either vasospastic or non-vasospastic ischemia as a result of a hypersensitive response. The acute coronary symptoms of Kounis syndrome include coronary spasm, abrupt myocardial infarction, and stent thrombosis, which are induced by allergy or anaphylactic assaults.
People who have Kounis syndrome face significant dangers and problems as a result of the difficulty in diagnosing their condition. This condition can progress to significant problems if it is either not addressed or the diagnosis is delayed. Depending on how severe the illness is, these risks and symptoms might range from minor to life-threatening. The following are some of the signs of this disease:
- Allergy.
- Hypersensitivity.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Sluggish heartbeat.
- Wheezing.
- Breathlessness.
- Sweating.
- Ischemic heart disease.
- Swellings of the tongue and face.
- Drowsiness.
- Consciousness loss.
- Edema in the lungs.
- Seizures.
- Coronary arrest.
- Hypersensitivity shock.
- Returning to the hospital.
- Abrupt demise.
Kounis Syndrome ECG
ECG illustrates, via a graph, how the electrical activity of the heart fluctuates throughout a cardiac cycle. This helps us find more problems and get a better idea of how well the heart is working. A patient is connected to the machine by several electrical leads. These leads continually monitor the activity and function of the patient’s heart while the patient is attached to the machine. Every time an electrical impulse passes through the heart, the heart generates its electrical signals.
ECG abnormalities that are more common in people with Kounis Syndrome include the following:
- Bradycardia sinus.
- Nasal tachycardia.
- Atrioventricular fibrillation.
- Nodal beats.
- Depression or elevation of the ST segment.
- T wave flattening or inversion.
- QRS expansion.
- Extended QT period.
- Cardiovascular irregularities.
Kounis Syndrome Diagnosis
The underdiagnosis of Kounis syndrome is common. To effectively treat this illness, a comprehensive diagnosis is required first. Symptoms are used as a guide for the doctor when making a diagnosis of Kounis syndrome. The medical history and family history are often requested by the doctor. Blood tests are one such test, the other tests are as follows:
- A chest x-ray.
- MRI, ECG, and EKG.
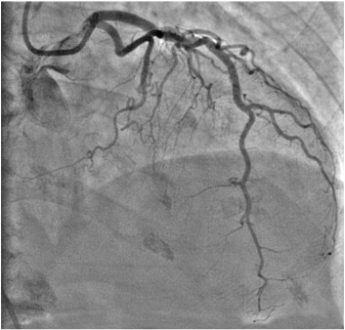
- Angiography.
To confirm the diagnosis, tests such as serum tryptase and histamine, immunoglobulin, cardia troponins, cardiac enzymes, etc. are also performed. SPECT is one example of a more recent diagnostic technology that is also used for diagnosing this disease.
Kounis Syndrome Causes
Although the true etiology of Kounis syndrome is unknown, allergic reactions and immune system reactions to vaccination medications or vaccines are the most common causes. The following factors can lead to this allergic disease:
- Aspirin and dipyrone.
- Anesthetics.
- Several antibiotics.
- Heparin and lepirudin are examples of anticoagulants.
- Antiplatelet medication, such as clopidogrel.
- Antineoplastics.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Analgesics that do not contain steroid hormones (NSAID)
- Skin sanitizers.
- Antifungals.
- Antivirals.
- Oral birth control.
- Other specific drugs include Insulin, Enalapril, Losartan, Allopurinol, and the like.
Kounis Syndrome Treatment
Elimination of the allergen that causes Kounis syndrome is followed by management of acute coronary vasospasm and allergy treatment. While treating the acute situation, it is necessary to select medications with caution and use them to prevent the release of more histamine and the worsening of coronary vasospasm.
Beta-lactam antibiotics are one of the drugs that are linked to Kounis syndrome. When treating myocardial infection-related acute chest pain, opiates including morphine, codeine, and meperidine are mostly administered with great caution. Thus, the prognosis for the patient with Kounis syndrome depends on factors such as the patient’s sensitivity, exposure to allergens, the severity of the initial allergic reaction, and environmental factors, as well as the condition’s variability.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information