Learn all about Colpocleisis surgery recovery, success rate, complications and cost. A colpocleisis operation involves sewing the front and back walls of the vagina together. This closes off the vagina and gets rid of the prolapse bulge. As the vagina is closed off, sexual intercourse is not possible after the operation. It is not suitable for women who are sexually active now or may wish to be so in the future.
The term colpocleisis is derived from the Greek words kolpos, which means folds or hollow, and cleisis, which means closure. The first report of colpocleisis occurred in 1823 when Gerardin described denuding the anterior and posterior vaginal wall at the introitus and suturing them. The technique currently used, however, is a modification of that first described in 1877 by Leon LeFort.
A colpocleisis can be done for women who have had a hysterectomy in the past or for those who still have their womb. It is a smaller operation than other operations offered for prolapse and, therefore, is often requested by older women who are troubled by lots of other medical problems.
If you have any medical problems, make sure that you are cleared for surgery (medicine or anesthesia). Make sure you have all the necessary lab work, EKG, or chest x-rays done at least 3 days before surgery.
Make sure your physician knows what medications, including herbal supplements, you are currently taking. Some Medications need to be stopped for some time before the procedure. Women seeking care for pelvic floor symptoms should undergo a thorough evaluation before having surgery. Those with pelvic organ prolapse may have coexisting pelvic floor disorders that may include defecatory dysfunction or urinary symptoms such as stress incontinence. Patients must therefore be questioned about any associated bothersome urinary or bowel symptoms because this may affect surgical planning.
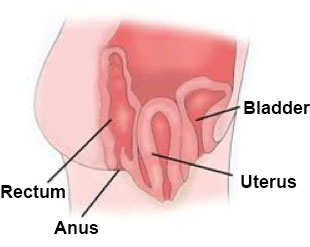
What is Colpocleisis
Colpocleisis is a procedure involving closure of the vagina. Colpocleisis involves the removal of vaginal epithelium and subsequent imbrication of the vaginal muscularis in anterior-to-posterior apposition, thereby creating a tissue septum of support. Variations in technique are based on the size and amount of epithelium removed.
Colpocleisis Surgery
Colpocleisis or total vaginectomy can be performed in women who develop prolapse after having undergone a prior hysterectomy or can be performed in conjunction with a hysterectomy. It involves removing the vaginal epithelium (lining of the vagina) with subsequent closure of the vagina. Permanent sutures are used to place sequential purse-string stitches that ultimately reduce the vaginal prolapse. In the case of a woman with a uterus, it is performed after completion of a vaginal hysterectomy.
Colpocleisis Recovery
Delayed return to normal activity may be especially costly among elderly women because of the risk of venous thromboembolism. Because of the high failure rate, slow recovery, and risk of complications, reconstructive surgery may not be as appropriate as colpocleisis for the woman described above. Colpocleisis suturing the inside walls of the vagina together has an efficacy rate exceeding 90%. Typical recovery time is one overnight stay at the hospital. While pain tolerance is variable among patients, most patients report minimal pain after a colpocleisis. Overall recovery time includes six weeks with some activity restrictions however patients are often able to return to a normal routine shortly after surgery.
Colpocleisis Success rate
The retrospective studies show that women who underwent colpocleisis operations are satisfied with the results of their management. The satisfaction rate was over 90%, with an anatomical success rate over 95%, which is consistent with previously reported anatomical success rates between 91% and 100%.
Colpocleisis Complications
Complications from a colpocleisis are typically very low. However with every procedure there always some risks including anesthesia problems, postoperative pain, intraoperative bleeding, infection, blood clots and damage to adjacent organs. With regards to the colpocleisis, some specific risks include the following:
- 5-10% risk of postoperative urinary tract infection
- Feelings of regret
- Anaesthetic Risks: The risk from having an anaesthetic is usually small unless you have certain medical problems.
- Bleeding: The risk of serious blood loss is very small and it is rare that we have to give a blood transfusion after prolapse operations.
- However, your risk of bleeding may be higher if you are taking an anti-clotting medication such as Warfarin. It is very important that you share with us any religious objection you may have to receiving blood in a life threatening emergency.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the wound site or in your bladder, which is reduced by giving you a dose of antibiotics during the operation. The risk of a serious infection is very small. You will be screened for MRSA at your preoperative check by taking some skin swabs.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This is a clot in the deep veins of the legs. The risk of a DVT is about 4 in 100 and many cause no symptoms. In a very small number of cases, bits of the clot can break off and get stuck in the lungs causing a serious condition (pulmonary embolism PE). The risk of a DVT is higher in women who smoke or who are overweight. The risk can be reduced by wearing special stockings and sometimes using injections to thin the blood. Pain: Mild pain for a few days or weeks after the operation is normal as the wounds from surgery heal. Some women also have increased back or hip pain after vaginal operations as we need to position you with your legs in stirrups to perform the operation. Rarely, more severe or long-lasting pain can develop after surgery, even when the operation has otherwise been successful. There are many reasons for this and it is not always possible to resolve it.
- Worsening or persisting problems with your bladder or bowels
Colpocleisis Cost
Most insurance policies will cover Le Fort colpocleisis. The procedure cost: $3,895.00 only.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information