Omental diseases have a wide range of symptoms which can be simple inflammation or chronic infection. In a few cases, it is malignancy. Usually, the primary tumor of the omentum is considered a malignancy. It can also spread to the nearby regions or organs of the body.
Seedlings and infiltration are included in the patterns of Omental caking. Omental caking is the thickening of the solid mass of the omentum. The advanced stage of any disease is evaluated by the thick omental caking. Omental caking is reported with a wide range of tumors which include metastatic peritoneal tumors, adenocarcinoma of the colon.
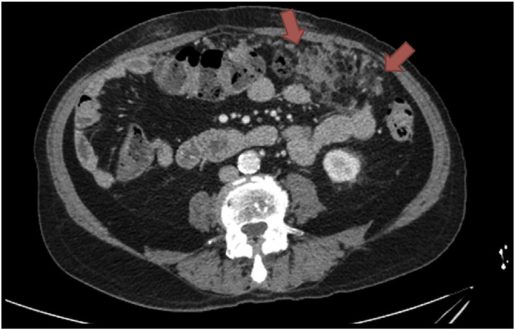
Omental caking is common in adults. When we talk anatomically, the thick bands of fatty tissue with blood vessels are called the omentum. This thick mass is easily identified through a CT scan. Children are rarely affected by this condition. But in cases like rhabdomyosarcoma and tuberculosis, it is reported that omental caking can be seen.
Omental Caking Symptoms
The detection of omental cake in the early stages is hard. The main reason is that the symptoms are considered vague and this makes it difficult to diagnose. Malignancies are most commonly associated with omentum. When the symptoms experienced by the patient are clear, it means that the disease has progressed to the advanced stages.
Omental caking is linked to various types of malignancies. But the symptoms vary with the kind of tumor. Multiple diagnostic tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis of omental caking. A few of the symptoms commonly experienced by these patients are as follows:
- Indigestion or abdominal discomfort, swelling, bloating, and abdominal cramping
- Nausea
- Diarrhea which can be chronic
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Excess weight gain and weight loss that is unexplained
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Rectal bleeding
- Feeling of fullness after light meals. It can lead to loss of appetite
Omental Caking Causes
Numerous causes can lead to omental caking. The subdivision of these causes are as follows:
Metastasis(Common cause)
- Carcinoma of colon
- Ovarian carcinoma
- Pancreatic carcinoma
- Gastric carcinoma
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Endometrial carcinoma
- Bladder cancer
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Hepatobiliary malignancies
The omentum can spread through different routes which involve hematogenous spread, direct extension, lymphatic spread, and intraperitoneal seeding.
Benign Tumors
- Lipoma
- Liposarcoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- Leiomyoma
- Abdominal mesothelioma
- Neurofibroma
Infections
- Tuberculosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Actinomycosis
- Mycobacterial infection
- Omental paragonimiasis
Some unusual reasons can lead to omental caking. These causes include myelofibrosis, amyloidosis, and sclerosing omentitis.
Omental Caking Radiology
The amount of fat in the omentum will vary with the size. The width of the omental cake is variable. The extent of the disease will be visible in the CT scan. The band of fatty tissue has a smudged appearance. Soft tissue nodules are enhanced when the disease progresses.
The normal fat is replaced when the omental rises abnormally. The cause of this condition is equally important to discover the severity of this condition. Ascites can be associated along with omental caking. The omentum, which is enormous, is seen as a big mass with lymphatics and milky spots. The clearance of pathogens is dependent on these milky spots.
It can extend to the pylorus or further to the small bowel or further to the posterior mesocolon.
Omental Cake Prognosis
A CT scan is the first diagnostic tool used for the diagnosis of Omental caking. If the images are not clear or any supporting evidence is needed, then MRI is used. Gastrointestinal contrast should be administered before MRI. Iodinated IV contrast material is used in imaging to get a clear picture of the thickness of the omentum.
Patients who are contraindicated to CT scans can easily rely on MRI. The presence of the intrahepatic findings can lead to the discovery or prognosis of omental cake. Many conditions can lead to omental caking. Percutaneous biopsy is used for specified diagnosis.
The prognosis is dependent on the main point that whether the omental cake is associated with tumor, inflammation, or any malignancy. The treatment plan is devised after confirmation.
Omental Cake Treatment
Diagnosing omental tumors may take some time due to the confusing symptoms. Various clinical reports suggest that chemotherapy would be highly beneficial for patients who suffer from omental caking. Medication therapy may include doxorubicin alone or in conjunction with other therapies.
The response rate for these treatment strategies is around 80%. Sometimes the recommended course is for 12 months which might include the above therapy with the additional sessions of chemotherapy. Intraperitoneal cisplatin has also been used to treat the malignancies related to omental cake treatment.
 Health & Care Information
Health & Care Information